Partnering to Create an Innovative In-Demand Baccalaureate Degree

In fall 2024, Cuyahoga Community College (Tri-C) began offering its first bachelor’s degree: a Bachelor of Applied Science in integrated digital manufacturing (IDM) engineering technology. To understand why Tri-C developed a four-year IDM degree, we need to look at some historic and recent economic data about Northeast Ohio.
Ohio has held a notable position in the manufacturing sector, typically ranked number three in the U.S. with over 14,000 manufacturing companies (IndustrySelect, 2024). More importantly, Northeast Ohio is a crucial player within the state, with over 6,000 manufacturers in the region alone. Manufacturing is the most significant contributor to the state GDP, contributing over $126 billion in 2023 (Ohio Manufacturers’ Association, 2024).
Research on smart manufacturing revealed its potential to significantly boost the manufacturing GDP in Northeast Ohio, adding from $3.5 to $13 billion annually (Team NEO, 2020). This paves the way for a promising future in the industry, filled with opportunities for growth and development.
Tri-C recognizes that Northeast Ohio's economy is heavily dependent on manufacturing. Regional companies specialize in advanced manufacturing, automotive parts, and other high-value industries. The region’s manufacturing sector includes many small and medium-sized enterprises as well as larger industrial firms that provide meaningful employment for the area’s economy.
Tri-C is deeply committed to understanding and meeting the needs of our local industries, supporting their growth, and helping them maintain their competitiveness in their respective markets. We are here for them as an integral part of our community, providing unwavering support that, in return, will help our community members obtain meaningful and rewarding careers.
Recognizing the need for a skilled workforce throughout various industries in the state, the Ohio legislature, in its 2017 biennial budget, included a provision allowing community colleges to offer certain applied bachelor’s degrees (Kyaw, 2024). Aside from the curriculum and academic program information, community colleges were required to provide the Ohio Department of Higher Education (ODHE) with information on (1) way(s) the proposed four-year degree would meet a workforce need not being addressed by existing programs, (2) agreements with local business and industry support for the degree, (3) way(s) the program would include workplace-based learning, and (4) institutional resources available to support the new program. Additionally, applications were posted on the ODHE site for public comment by four-year institutions that may have similar programs in the same geographic area.[1]
Ohio is not the only state that has recognized the need for community colleges to provide credentials past an associate degree level. The Community College Baccalaureate Association, which assists community colleges throughout the nation in providing accessible bachelor’s degrees to their students, noted that as of June 2024, 191 U.S. community colleges were authorized to confer bachelor’s degrees (Kyaw, 2024). Research has also shown that almost half of the community colleges that offer bachelor’s degrees are classified as Minority Serving Institutions (MSI), with 71 percent of those with MSI designation also being Hispanic Serving Institutions (Kyaw, 2024). Additionally, women made up 64 percent of the graduates at 64 percent of the colleges authorized to award bachelor’s degrees (Kyaw, 2024).
Realizing there was a need for a skilled workforce credential beyond an associate degree in Northeast Ohio and that Tri-C was uniquely positioned to address this gap, our workforce division initiated discussions with a regional cross-section of small, medium, and large manufacturers. The goal was not only to understand employer needs, challenges, requirements, and plans for future growth, but also to work together in a spirit of collaboration and shared responsibility.
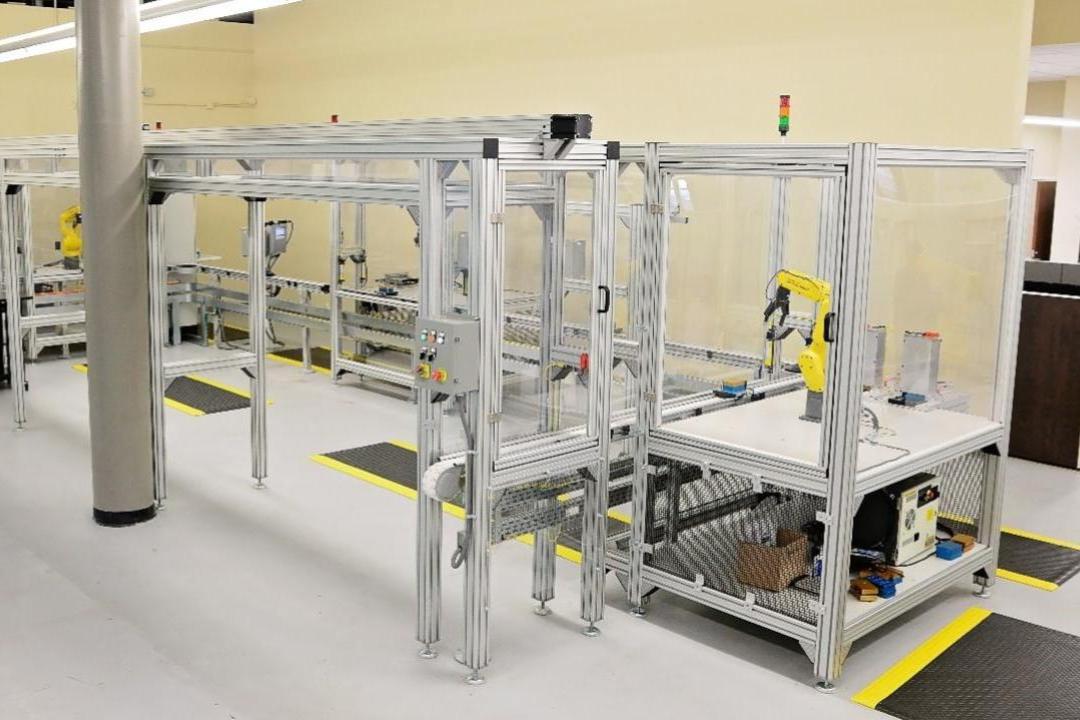

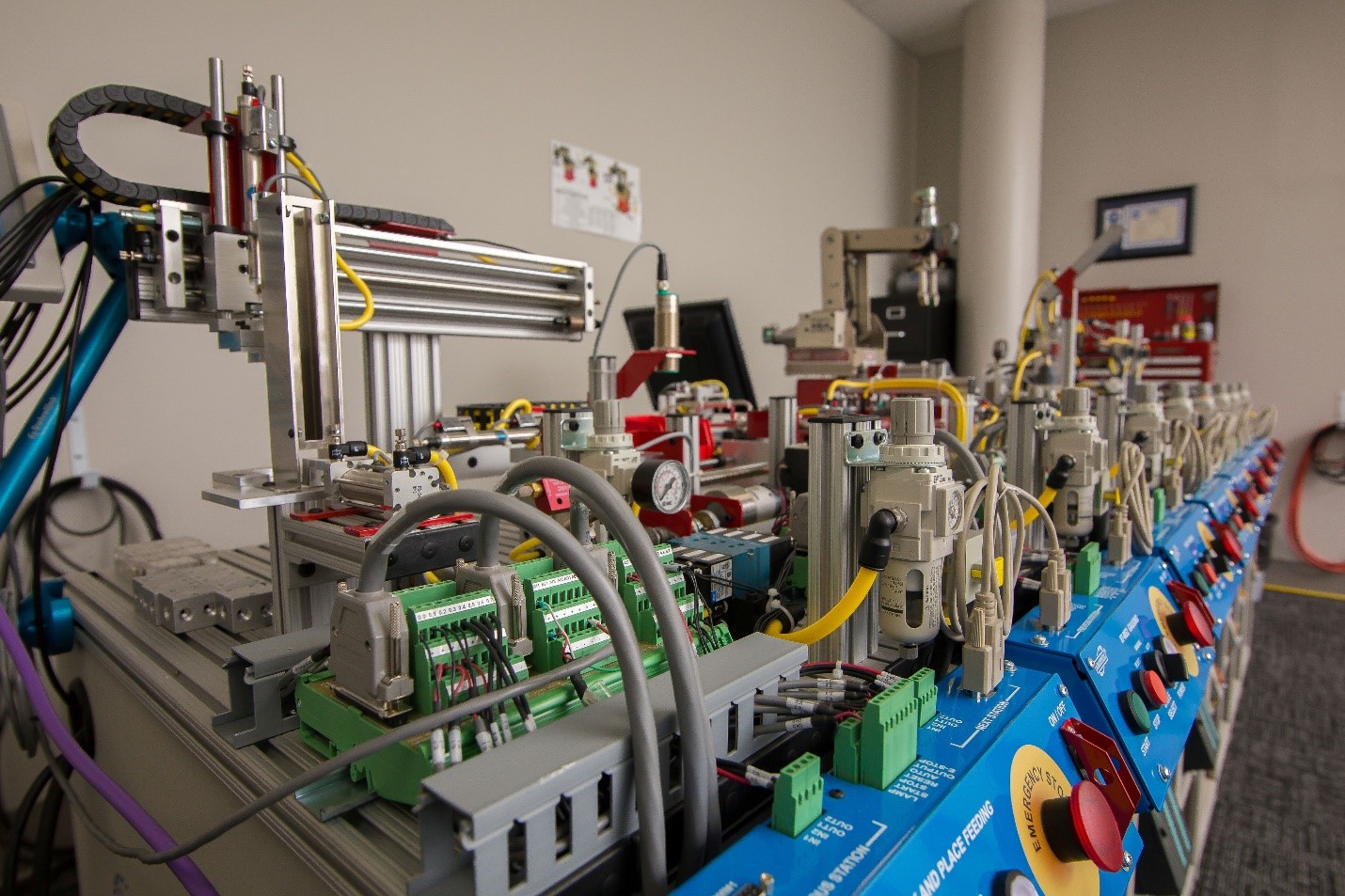
This integrated systems workstation is used both in Tri-C’s A.A.S.
and integrated digital manufacturing technology B.A.S. programs.
Regional manufacturers informed Tri-C that in order to become more competitive in the market, they needed a workforce trained in smart manufacturing skills, including Industry 4.0 technologies, Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, robotics, and advanced analytics. By employing these technologies, companies noted they could continue to enhance operational efficiencies, reduce downtime, and improve production capabilities. The integration of smart manufacturing technologies had the potential to allow Northeast Ohio manufacturers to compete on a national and global scale.
The employers articulated that this new workforce also required additional knowledge in automation design, troubleshooting, machine connectivity, and cybersecurity. By leveraging Industry 4.0, Northeast Ohio would see an expansion in its manufacturing base with new investments and business opportunities, but to achieve this growth, employers needed a skilled workforce with smart manufacturing credentials.
After confirming the industry's challenges and noting that no regional four-year institution addressed the need for a trained workforce in smart manufacturing, Tri-C started the work of developing a bachelor’s degree that would provide training in areas of technology in manufacturing processes, Industry 4.0 concepts, cybersecurity, robotics, autonomy, automation, lean manufacturing, Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), and supply chain management. The four-year degree was intended to build on several of Tri-C’s existing associate degrees, one of which was a newly approved Associate of Applied Science in smart manufacturing. Inclusion of experiential learning opportunities, such as co-ops and internships, was critical, as was a course progression that facilitates upskilling current employees working in the field. To that end, the course modalities had to provide access for full-time, underemployed, and off-shift workers to engage, learn, and improve their economic position while helping the region grow.
Tri-C submitted its comprehensive application for the bachelor’s degree to ODHE in 2022. The development was a collaboration of Tri-C faculty; industry experts; service providers for industry, federal, state, and local government initiatives; the community; and Tri-C students. The application provided an in-depth discussion of the proposed curriculum as well as the credentials awarded within the pathway to completion. Additional information included evidence of the unmet regional workforce need. Supporting evidence included job postings, letters of partnership from local employers confirming the lack of skilled workers in this area, and a confirmed desire by industry to hire graduates of the new bachelor’s program. Finally, evidence of Tri-C’s institutional capacity to acquire technology and support the program with reallocated finances and additional faculty was provided per the application requirements.
In June 2022, Tri-C received ODHE approval to offer its Bachelor of Applied Science in IDM. After securing Higher Learning Commission approval and the needed accreditation from ABET, the applicable organization to accredit computing, engineering, and engineering technology programs in higher education, Tri-C welcomed students into its inaugural applied bachelor’s degree program in fall of 2024. Students completing this degree will gain a comprehensive knowledge of manufacturing and automated systems, mechanical devices, electrical issues, industrial information technology, and networking. Students will also leave the program with hands-on operational knowledge, allowing them to manage these manufacturing processes for area employers.
The IDM degree contains over 20 industry certifications that can be earned as a student moves from entry to completion or by a student entering the program simply to obtain one or more credentials. Creating this type of course sequence also allows students to stack credentials as they move through the program. This will help students who attend part-time to gain employment in the sector as they work on the degree.
The IDM degree uniquely offers extensive hands-on training in Tri-C labs, which gives students the knowledge they need to move into a job immediately, with minimal or no additional training necessary. This training complements the program’s emphasis on experiential learning to meet local employer needs for students entering company co-op and internship programs. Adding even more flexibility, parts of the curriculum may be taken in remote modalities: Hands-on laboratory and on-ground courses are offered between 8:00 a.m. and 8:00 p.m. and on weekends to accommodate those who have family or employment obligations.
Ultimately, those who complete the IDM degree or earn additional certifications in the bachelor’s program will leave with marketable and in-demand real-world skills in human data input, robotics, programmable logic controllers, smart sensors, and devices. Additionally, students will learn theory and management of smart manufacturing utilizing IIoT and supervisory control and data acquisition software and hardware. They will also acquire knowledge of electrical, mechanical, networking engineering, cybersecurity, cloud security, enterprise security, and design knowledge, all of which are essential parts of the program.
In essence, Tri-C has developed a groundbreaking program designed to empower graduates by equipping them with the skills to effectively bridge the gap between various disciplines. By doing so, they can facilitate better understanding and collaboration among experts from different fields. Additionally, the program aims to cultivate graduates who are capable of leading complex, multi-disciplinary projects with efficiency and finesse. Tri-C’s IDM degree has also addressed the needs of individuals who aspire to improve their circumstances but are hindered by the need to work and provide for their families, thereby lacking the means to pursue further education.
References
IndustrySelect. (2024, May). Top 10 U.S. states for manufacturing. Top 10 U.S. states for manufacturing. https://www.industryselect.com/blog/top-10-us-states-for-manufacturing
Kyaw, A. (2024, May). Report: Increasing numbers of community colleges are offering bachelor’s degrees. Diverse: Issues in Higher Education. https://www.diverseeducation.com/students/article/15670317
Ohio Manufacturers’ Association. (2024). Manufacturing counts: Facts about the economic impact of Ohio manufacturing. https://www.ohiomfg.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/OMA-Manufacturing-Counts-2024-Final-Version.pdf
Team NEO. (2020). Smart manufacturing Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): Roadmap for Northeast Ohio. https://northeastohioregion.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/smart-manufacturing-iiot-roadmap-executive-summary-2020.pdf
Lead image: Located adjacent to Tri-C's Metro campus, the Manufacturing Technology Center is one of the largest technology training facilities in the country.
Ray Nejafard is Dean, Advanced Manufacturing and Engineering, at Cuyahoga Community College in Cleveland, Ohio.
Opinions expressed in Innovation Showcase are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect those of the League for Innovation in the Community College.